Currently Empty: $0.00
Direct Material Price Variance Formula Example
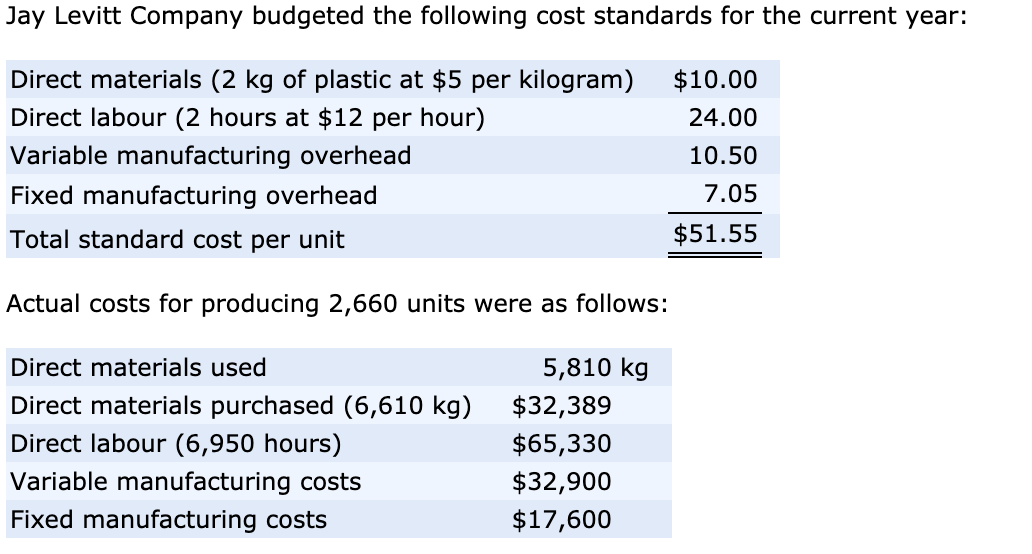
The difference between the standard cost (AQ × SP) and the actual cost (AQ × AP) gives us the material price variance amount. You multiply the actual quantity of materials bought by the difference between standard and actual price per unit. The following equations summarize the calculations for direct materials cost variance. The valuation of stock on standard cost basis implies that the entire effect of any price variance is to be accounted for in the current period. Therefore, the purchase cost of the entire quantity must be compared with the standard cost of the actual quantity. The actual price must exceed the standard price because the material price variance is adverse.
Can a positive variance be bad for my business?
You need to know both the budgeted price and what you actually paid for each unit of material. The budgeted price is usually based on standard cost – what your company expects to pay per unit of material. Picture this—your direct materials end up costing more than expected, but you’re not sure why or by how much. That’s where understanding and computing the price variance becomes essential. However, someone other than purchasing manager could be responsible for materials price variance. For example, production is scheduled in such a way that the purchasing manager must request express delivery.
Identify potential causes
The material price variance is adverse because the actual price is higher than the standard. The material price variance in this example is favorable because the company was able to get the materials at a lower cost compared to the budget. The standard price of $100 per bag was allowed in the budget, but the purchase manager was able to source the materials from a cheaper supplier at the cost of $80 per bag. It could be because a company got a discount or faced a materials shortage.
Common Problems with Direct Material Price Variance
A solid grasp on them helps in maintaining tight cost control over materials procurement. It tracks if spending goes as planned how do i import last years tax return or if there are surprises needing attention. After figuring out how much material you used, it’s time to look at the prices.
Material Price Variance Favorable or Unfavorable
If actual prices for materials are lower than budgeted, the variance is favorable. That means the company spent less on materials than expected – a good thing! The result from this calculation gives you the direct material price variance for your accounting records. If materials cost more than planned, your variance will be negative, showing a loss against your standard cost.
Do you own a business?
Thus, the price variance tracks differences in raw material prices, and yield variance tracks differences in the amount of raw materials used. The left side of the DMPV formula estimates what the actual quantity of direct materials purchased should cost according to the standard price allowed in the budget. The right side of the formula calculates what the direct materials actually cost during the period. The difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials, expressed as a positive or negative value, evaluated in terms of currency. The direct material price variance is favorable if the actual price of materials is __________ than the standard price.
Not necessarily; some variances are normal, but big ones need investigation to find the cause and fix it. This suggests spending more and hints at possible issues with purchasing decisions or market changes. Now, let’s delve into an example to better understand how the calculator functions.

Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links.
The following sections explain how management can assess potential causes for a favorable or adverse material price variance and devise a suitable response to the variation. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. Knowledge of this variance may prompt a company’s management team to increase product prices, use substitute materials, or find other offsetting sources of cost reduction. As you can see from the list of variance causes, different people may be responsible for an unfavorable variance. For example, a rush order is probably caused by an incorrect inventory record that is the responsibility of the warehouse manager. As another example, the decision to buy in different volumes may be caused by an incorrect sales estimate, which is the responsibility of the sales manager.
- The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process.
- Reliable suppliers who consistently deliver quality materials at agreed-upon prices help maintain stable production costs.
- This setup explains the unfavorable total direct materials variance of $7,200 — the company gains $13,500 by paying less for direct materials, but loses $20,700 by using more direct materials.
- Building strong relationships with suppliers and regularly evaluating their performance can help businesses anticipate and address potential problems before they impact production.
- It also shows that the actual price per pound was $0.30 higher than standard cost (unfavorable).
The total price variance during January is $ 200 ($ 400 – $ 300 + $ 100), and it will impact the cost of goods sold in statement of profit and lose. We can simplify the DMPV formula by multiplying the actual purchase quantity by the price difference, as shown below. This step shows the total impact on your budget due to changes in material costs. This process helps pinpoint where costs are not aligning with your financial plans and aids in maintaining control over spending.


